Welcome to Carjiajia!
+86-15962981422 +8613306508351(WhatsApp)
carjiajia2025@gmail.com
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-15 Origin: Site









No, not all electric car chargers work the same way for every driver. You will notice differences in speed, cost, and where you can use each type. Some chargers add just a few miles per hour, while others can give you over 100 miles in less than half an hour. Your choice depends on your car, how far you drive, and if you plan to charge at home or on the road. > Think about your driving routine and where you want to plug in before picking the best option.
Electric car chargers are not all the same. Pick one that fits how you drive and charge your car. Level 1 chargers are slow but good for short daily trips. Level 2 chargers work faster and are great for home charging. DC Fast Chargers give quick power for long trips. They can add up to 20 miles in one minute. Always look at your car's connector type. This helps you use the right charging station. Buying an ENERGY STAR certified charger saves money and energy. It also helps the environment.

When you look for electric car chargers, you will find three main types. Each type works differently and fits different needs. You can see the main differences in the table below.
Charger Type | Voltage Requirement | Power Output (kW) | Range per Hour (miles) |
|---|---|---|---|
Level 1 | 120 volts | 1.2 - 1.8 | 4 - 5 |
Level 2 | 240 volts | 7.2 - 19.2 | Faster than Level 1 |
Fast Chargers | Varies | 50 - 350 | Much faster |
Tesla Superchargers | Varies | Specific to Tesla vehicles | Very fast |
Level 1 chargers use a standard household outlet. You can plug them in at home without special equipment. These chargers work slowly, adding about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour. If you drive short distances each day, Level 1 may be enough for you.
Tip: Level 1 chargers take a long time to fully charge your car. You may need up to 71 hours for a full charge, so plan ahead if you use this option.
Level 2 chargers need a 240-volt outlet, like the one for a clothes dryer. These chargers work much faster than Level 1. You can add 20 to 30 miles of range per hour. Most home charging stations use Level 2 chargers. You can charge your car overnight and wake up with a full battery.
Here is a quick look at charging speeds:
Charger Level | Electrical Output | Range per Hour of Charging | Full Charge Time |
|---|---|---|---|
Level 1 | 1.3 kW to 2.4 kW AC | 3.11 miles | Up to 24 hours |
Level 2 | 3 kW to under 20 kW AC | 20 to 30 miles | Overnight |
Level 3 | 50 kW to 350 kW DC | Up to 20 miles per minute | Under 1 hour |
Many top home chargers for 2025 come from brands like Shell Recharge, Tesla, ChargerPoint, Blink Charging, Clipper Creek, and Leviton. These brands offer features such as high amperage, smart management, and ENERGY STAR certification. ENERGY STAR certified chargers help you save money and energy by working more efficiently.
DC Fast Chargers, also called Level 3 chargers, work much faster than Level 1 or Level 2. You can find these chargers at public stations, not usually at home. DC Fast Chargers can add up to 20 miles of range per minute. You can get a full charge in under 20 minutes. These chargers help you on long trips or when you need a quick boost.
Note: Not every car can use DC Fast Chargers. Check your car’s manual before you try one.
You need to choose the right charger for your lifestyle. If you drive a lot, a Level 2 or DC Fast Charger will save you time. If you only drive short distances, Level 1 may work for you. Government incentives help more people use electric car chargers by supporting new charging stations. Building more fast-charging stations can increase electric car use and lower emissions.
Top Home Charger Brands for 2025:
Shell Recharge
Tesla, Inc.
ChargerPoint
Blink Charging
Clipper Creek
Leviton
SemaConnect
FreeWire Technologies
BorgWarner
Nuvve Holding Corp.
Choosing an ENERGY STAR certified charger can help you save on electricity bills and protect the environment.
You will find that not all electric car chargers use the same connector. The connector type matters because it decides if your car can plug in and charge. Different car brands and regions use different connectors. If you know your car’s connector, you can avoid problems at public charging stations.
You will see the J1772 connector at most public and home charging stations in North America. This connector works for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging. Most electric cars, except Tesla, use J1772 for everyday charging. J1772 is simple and reliable, but it does not support fast DC charging. If you drive a car with a J1772 port, you can use almost any public charger for regular charging.
Note: J1772 is great for daily charging, but it cannot handle the fastest charging speeds.
The CCS connector builds on the J1772 design. It adds two extra pins for DC fast charging. This means you can use CCS for both slow AC charging and fast DC charging. Many new electric cars in the United States and Europe use CCS. If your car has a CCS port, you can charge at more places and get faster charging when you need it.
CHAdeMO is another connector for DC fast charging. You will find it mostly in Japanese cars, like the Nissan Leaf. Its use is common in Japan, but it is less popular in other regions. Here is a quick look at where you will find CHAdeMO:
Region | Usage of CHAdeMO Connectors |
|---|---|
Japan | Predominantly used |
Europe | Declining usage |
USA | Very few new cars |
China | Primarily for Japanese cars |
If you drive a car with a CHAdeMO port, you may have fewer charging options outside Japan.
Tesla uses its own connector for both home and public charging. In the United States, you will find over 12,000 Tesla Destination ports. Tesla drivers can use these stations, but other cars cannot use Tesla connectors without an adapter. Tesla’s network is large and fast, which makes charging easy for Tesla owners.
Tip: Always check your car’s connector type before you travel. The wrong connector can stop you from charging.
You can use apps like PlugShare, ChargePoint, and Electrify America to find stations that match your car. PlugShare lists over 140,000 charging stations worldwide. These apps help you plan your route and avoid compatibility issues.

When you install a home charger, you gain control and convenience. You can plug in your car overnight and wake up to a full battery. Home chargers usually cost less to use than public stations. On average, you pay about $0.14 per kWh at home. You also avoid waiting in line or dealing with broken equipment. Many people choose home chargers for their lower running costs and secure charging environment. You can find top-selling home chargers on Amazon, such as:
Rank | Product Name | Rating | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | EVIQO Level 2 EV Charger 40 Amp | 4.8 out of 5 stars | $517.22 |
2 | ChargePoint HomeFlex Level 2 EV Charger | 4.2 out of 5 stars | $927.44 |
3 | Grizzl-E Classic, Level 2 240V / 40A Charger | 4.6 out of 5 stars | $453.69 |
Tip: Home charging gives you full control over when and how you charge your car.
Public charging stations help you when you travel or need a quick boost. You find these chargers in parking lots, shopping centers, and along highways. In places like Myrtle Beach, you can access 124 public charging stations, with 68 of them free to use. Public chargers often include fast DC options, which can charge your car much faster than home units. However, public charging costs more—between $0.40 and $0.80 per kWh. You may also need to wait for a spot or use an app to start charging.
Type of Charging Station | Total Number | Free Stations |
|---|---|---|
Level 2 | 105 | 68 |
Level 3 (DC Fast) | 19 | 0 |
Total | 124 | 68 |
Note: Public charging is great for long trips but can be three times more expensive than charging at home.
You can install a home charger with help from a licensed electrician. This one-time investment gives you easy access and lower costs over time. Public chargers do not need installation, but you depend on their availability. Sometimes, you may face queues or find a charger out of service. To locate public stations, use online tools like the Alternative Fuels Data Center in the U.S. or Chargemap in Europe. These tools help you plan your route and find working chargers.
Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|
Alternative Fuels Data Center | Find electric vehicle charging stations in the United States/Canada |
Chargemap | Largest map for charging stations in Europe |
Remember: At-home charging is the most affordable and convenient way to keep your car ready, but public chargers are essential for travel and emergencies.
You need to check if your car matches the charger before you buy. Every electric vehicle has its own plug type, power rating, and way of talking to the charger. If you pick the wrong charger, your car may not connect or charge at all. Here are some things to look for:
Your car’s plug type decides which chargers you can use.
Some cars, like the Nissan Leaf, use a special connector. Most other cars use type 2 chargers.
Power ratings and communication methods also matter. Always check your car’s manual.
Tip: Make sure your charger matches your car’s plug and power needs. This helps you avoid problems later.
Charging speed depends on many things. The size of your battery, the charger’s voltage, and even the weather can change how fast your car charges. You can see the main factors in the table below.
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Battery Capacity and State | Bigger batteries take longer. Charging slows down as the battery fills up. |
Charging Infrastructure/Voltage | Higher voltage means faster charging. Level 2 chargers work between 240 and 415 volts. |
Environmental Conditions | Cold weather slows charging. Hot weather can also reduce speed to protect the battery. |
Vehicle Make and Model | Each car charges at its own speed. Check your car’s specs for details. |
Where you charge your car affects your daily routine. Many retail stores now offer charging stations, making it easy to charge while you shop. About 90% of drivers buy something while their car charges, which helps local businesses. If you do not have a home charger, public stations are important. Some households need special solutions because they cannot install chargers at home.
Note: Choose a charger that fits your lifestyle and charging locations.
Cost matters when you pick electric car chargers. Home chargers cost about $400 a year to maintain. Public DC fast chargers cost almost twice as much because they are more complex. You should also think about energy waste and long-term savings. ENERGY STAR certified chargers use less energy and save you money over time.
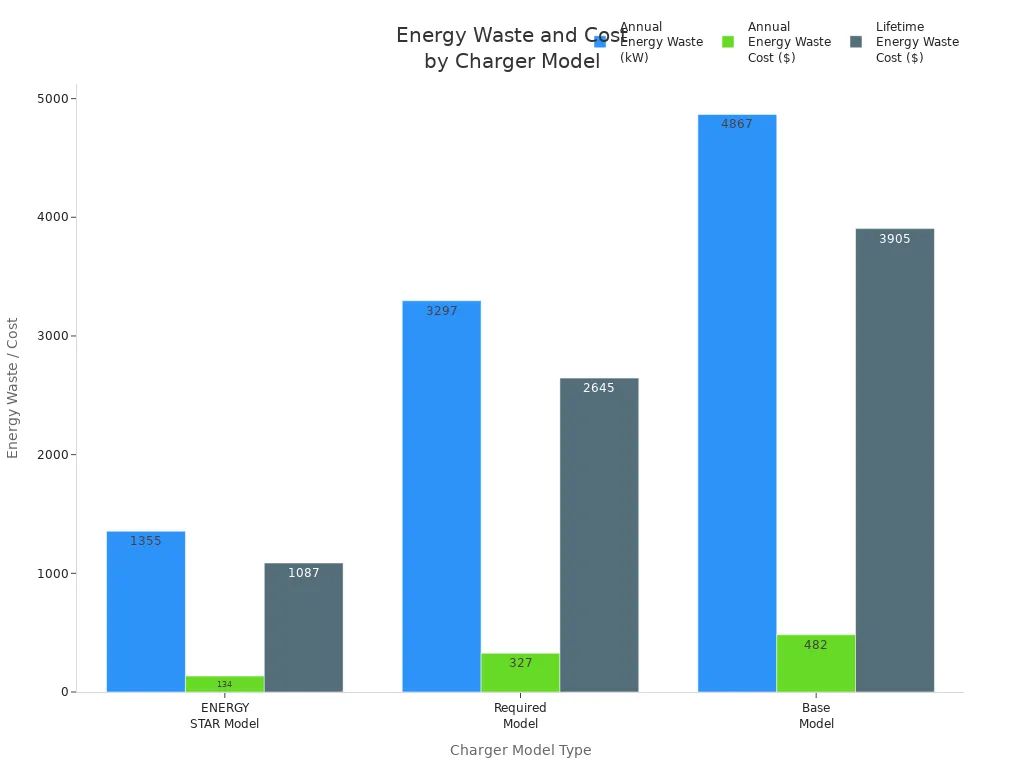
Model Type | Annual Energy Waste (kW) | Annual Energy Waste Cost | Lifetime Energy Waste Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
ENERGY STAR Model | 1,355 | $134 | $1,087 |
Required Model | 3,297 | $327 | $2,645 |
Base Model | 4,867 | $482 | $3,905 |
Choosing ENERGY STAR certified chargers helps you lower your carbon footprint and save money.
Common mistakes to avoid:
Using only the slow charger that comes with your car.
Spending too much on smart features you do not need.
Forgetting to check cable length.
Not planning for future needs, like more EVs in your home.
Always think about your car’s connector type, charging speed, and budget before you buy.
You have learned that electric car chargers are different. Picking the right charger makes your life easier. It also helps your car’s battery last longer.
Smart charger choices stop you from wasting time. They also keep your battery in good shape.
Fast charging and using portable chargers can help your car sell for more money later.
Easy-to-use features make charging simple and less stressful.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Cost Savings | Charging at home costs less and skips public station fees. |
Increased Property Value | Homes with EV chargers are more attractive to buyers. They can also be worth more money. |
Environmental Benefits | Charging at home can use clean energy and helps the planet. |
Enhanced Charging Speed | Level 2 chargers fill your battery faster for busy days. |
Improved Safety | Having a pro install your charger keeps things safe. |
Energy Independence | You can use your own solar or wind power for your car. |
Support for Future Technology | You can upgrade home chargers for new EV features. |
Take time to think about what you need and what your car needs. Knowing about charger types makes owning an electric car easier and more fun.
Level 1 chargers use regular outlets and charge slowly. Level 2 chargers need special outlets and charge much faster. You can fill your battery overnight with Level 2.
You need to check your car’s connector type. Some chargers work for most cars, but others only fit certain brands. Always match the charger to your car before plugging in.
You can use apps like PlugShare or ChargePoint. These apps show you nearby stations and tell you which ones fit your car. You can plan your trip and avoid running out of power.
Home charging usually costs less than public charging. Fast chargers at public stations cost more because they work quickly. You save money by charging at home when you can.
ENERGY STAR certified chargers use less energy. You save money on electricity and help the environment. These chargers work efficiently and protect your battery.